What Is Class A B C D Airspace
ATC service traffic INFO on all other flights. Class G airspace is essentially uncontrolled by ATC except.

Differences Between Airspace Classifications Cal Aero Blog
The airspace around the least busy airports that still require an ATC control tower.

What is class a b c d airspace. Class E airspace starts at various altitudes but always. Class G is considered uncontrolled In Class G airspace pilots are solely responsible for their own navigation and separation from traffic terrain and obstructions. 15 lignes ATS airspace is classified and designated in accordance with the following.
A generic term that covers the different classification of airspace ClassA ClassB Class C Class D and Class E airspace and defined dimensions within which air traffic control service is provided to IFR flights and to VFR flights in accordance with the. Class G airspace is uncontrolled. Airspace within the given radius but in surrounding class C or class B airspace is excluded.
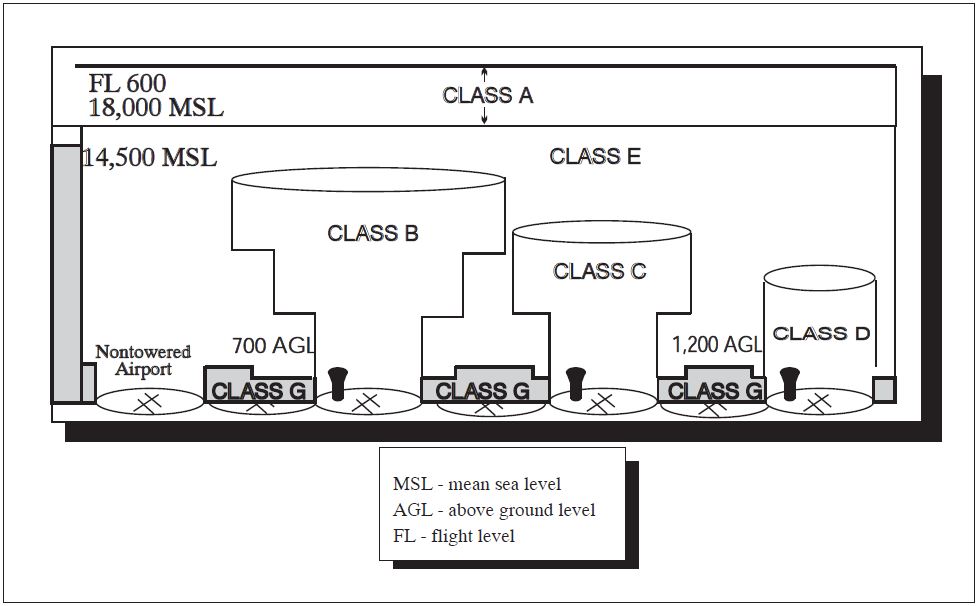
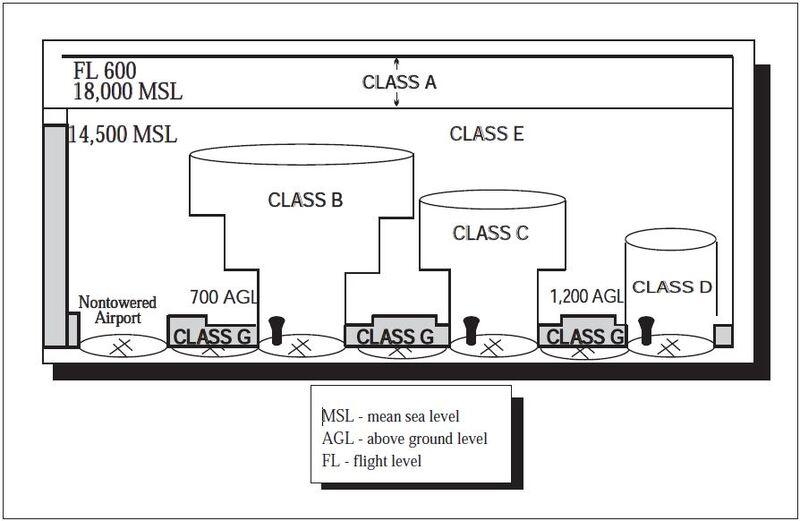
Generally from surface to 10000 feet mean sea level MSL including the airspace from portions of Class Bravo that extend beyond the Mode C Veil up to 10000 feet MSL eg. LAX LAS PHX Class C. Airspace within the given radius but in surrounding class C or class B.
Airspace within approximately 10 miles and 4000 feet of airports that are less busy than Class B airports. Class D airspace only has a surface area no shelf or outer area for radar surfaces. Class G Airspace not designated as Class A B C D or E.
The aim is to cover sufficient airspace to enable the safe control and separation of aircraft in IFR operations. IFR from IFR IFR from special VFR. Class D Airspace indicated by the dashed blue line.
ATC service traffic information about VFR flights. Class D airspace is generally cylindrical in form and normally extends from the surface to 2500 feet 760 m above the ground. The difference with Class D airspace as opposed to Class B or Class C airspace is that the primary airport in Class D has a control tower and provides weather reporting but does not provide radar services.
Classes A through E are all types of controlled airspace. Generally from surface up to 4000 feet MSL including the airspace above the horizontal boundary up to 10000 feet MSL. This is where air traffic control has various levels of jurisdiction.
Class D Airspace is around medium-sized airports and typically has a blue number inside of a blue box. Controlled airspace is provided primarily to protect its users mostly commercial airliners and as such aircraft which fly in controlled airspace must be equipped to a certain. 200 kt IAS at or below 2500 ft AAL within 4 nm of the primary Class D aerodrome see note 3 250 kt IAS in the remaining Class D airspace.
Above 10000 feet MSL. In controlled airspace air traffic controllers are responsible for separating aircraft. Unless otherwise permitted two-way radio communication must be established with ATC prior to entering the airspace and then maintained while flying in Class D airspace.
Class D airspace is generally cylindrical in form and normally extends from the surface to 2500 feet 760 m above the ground. You can learn more about the different types of Class E airspace by referring to the Aeronautical Information Manual AIM. Classes A C D and E are areas of controlled airspace and G is uncontrolled airspace.
Class F is does not exist over the United States. It is approximately 4 miles and 2500 feet of airspace and they usually dont have radar so just. In the United States airspace is divided into Class A B C D E and G.
In the example image above the blue number in the box is 30 meaning the airspace ceiling extends up to 3000 feet. In the United States Class A B C D and E airspace is controlled. Is the controlled airspace not classified as Class A B C or D airspace.
Its the controlled airspace that is not categorized as class A B C or D. Note that while an operating control tower usually is indicative of at least a Class D airspace there are a few airports with operating control towers that are not considered Class D. Unless designated at a lower altitude Class E airspace begins at 14500 MSL over the United States including that airspace overlying the waters within 12 NM of the coast of the 48 contiguous states and Alaska up to but not including 18000 feet MSL and the airspace above FL 600.
Most of the airspace located across the US is designated as Class E. Class D airspace reverts to class E or G during hours when the tower is closed or under other special conditions. The equipment requirements are less restrictive to fly in this airspace and pilots must be talking to ATC.

Airspace Classes In 2021 International Civil Aviation Organization Class Class B

The Hidden Secrets Of Uk Airspace Airspace Classifications Nats Blog

Chapter 7 Canadian Airspace Pdf Free Download

Is It Required For Pilots To Contact Atc While Flying Vfr Aviation Stack Exchange

Instrument Flying Handbook Chapter 8 American Flyers Aviation Training Aviation Airplane Aviation Education

Proposed Faa Small Uas Rule What Is Class B C D And E Airspace By Ben Marcus Future Of Flight Medium

Ep 42 Class A Airspace Explained And Where It Is Youtube
Understanding Airspace For Paraglider Pilots
Airspace Air Traffic Control U Tapao Facebook
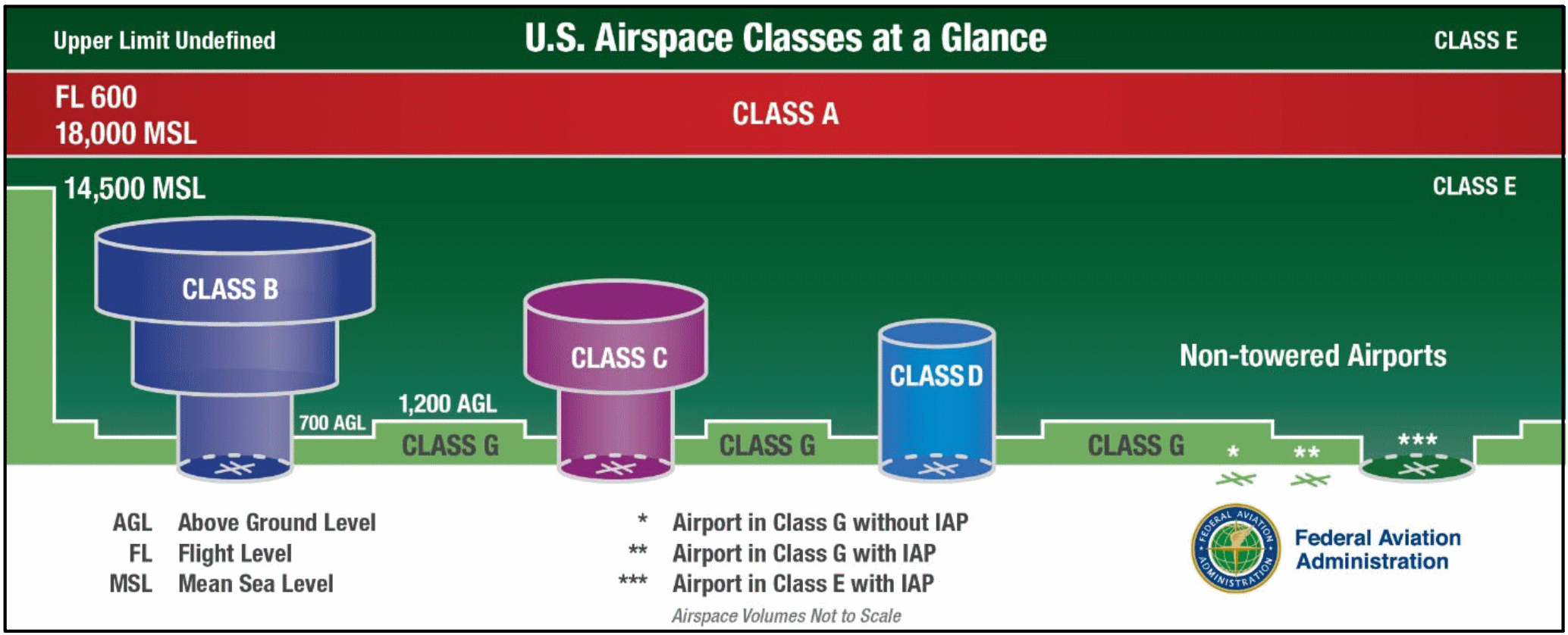
Differences Between Airspace Classifications Cal Aero Blog

Navigating Airspace Classifications When Where To Fly Your Drone
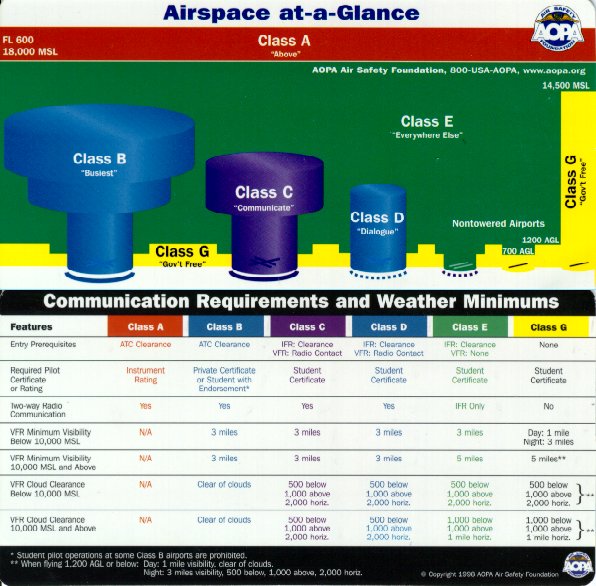
What S The Best Way To Remember Airspace Pilots Of America
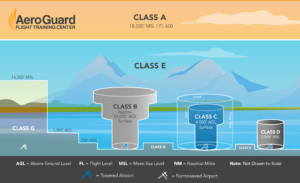
Airspace Classes How Are They Defined Aeroguard

How To Request Faa Airspace Authorization Drone Pilot Ground School
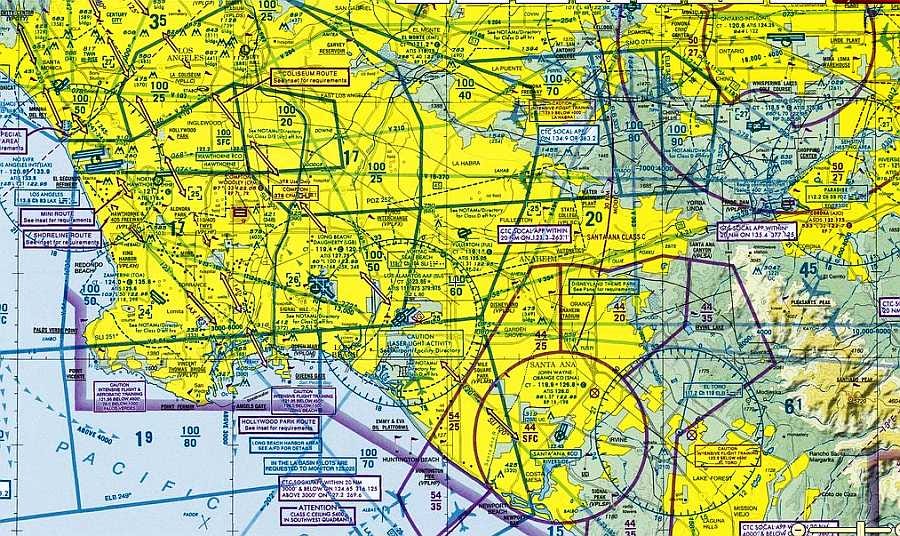
Proposed Faa Small Uas Rule What Is Class B C D And E Airspace By Ben Marcus Future Of Flight Medium


Posting Komentar untuk "What Is Class A B C D Airspace"